[SpringBoot] 파일 업로드/다운로드
파일 업로드/다운로드
전송 방식
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- multipart/form-data
application/x-www-form-urlencoded
이 방식은 HTML 폼 데이터를 서버로 전송하는 가장 기본적인 방법이다.
Form 태그에 별도의 enctype 옵션이 없으면 웹 브라우저는 요청 HTTP메시지의 헤더에 다음 내용을 추가한다.
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
그리고 폼에 입력한 전송할 항목을 HTTP Body에 문자로 username=kim&age=20 와 같이 & 로 구분해서 전송한다.
하지만 파일을 전송할 때에는 위와 같이 문자가 아닌 바이너리 데이터를 전송해야 한다. 심지어 파일을 보낼 때 파일만 보내는 경우보다 섞어서 보내는 경우가 더 많다. 이럴 때 필요한 전송 방식이
multipart/form-data이다.
multipart/form-data
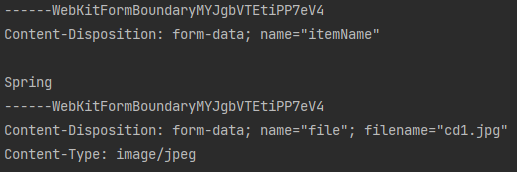
이 방식을 사용하려면 From태그에 별도의 enctype = “multipart/form-data”를 지정해야 한다. 이렇게 폼을 입력하면 그 결과로 생성된 HTTP 메시지에는 각각의 전송 항목이 구분이 되어있다.
Content-Disposition 이라는 항목별 헤더가 추가되어 있고 여기에 부가 정보가 있다. 폼의 일반 데이터는 각 항목별로 문자가 전송되고, 파일의 경우 파일이름과 Content-Type이 추가되고 바이너리 데이터가 전송된다.
서블릿 파일 업로드/저장
업로드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
@Slf4j
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/servlet/v2")
public class ServletUploadcontrollerV2 {
@Value("${file.dir}")
private String fileDir;
@GetMapping("/upload")
public String newFile(){
return "upload-form";
}
@PostMapping("/upload")
public String saveFileV1(MultipartHttpServletRequest request) throws ServletException, IOException {
log.info("request={}",request);
String itemName= request.getParameter("itemName");
log.info("itemName={}",itemName);
Collection<Part> parts = request.getParts();
log.info("parts= {}",parts);
for (Part part : parts) {
log.info("--- PART ---");
log.info("name = {} ", part.getName());
Collection<String> headerNames = part.getHeaderNames();
for (String headerName : headerNames) {
log.info("header {}: {}", headerName, part.getHeader(headerName));
}
//편의 메서드
// content-idsposition; filename
log.info("submittedFilename={}", part.getSubmittedFileName());
log.info("size = {} ",part.getSize()); //part body size
//데이터 읽기
InputStream inputStream = part.getInputStream();
String body = StreamUtils.copyToString(inputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
log.info("body ={}",body);
//파일에 저장하기
if(StringUtils.hasText(part.getSubmittedFileName())){
String fullPath = fileDir + part.getSubmittedFileName();
log.info("파일 저장 fullPath = {}", fullPath);
part.write(fullPath);
}
}
return "upload-form";
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="py-5 text-center">
<h2>상품 등록 폼</h2>
</div>
<h4 class="mb-3">상품 입력</h4>
<form th:action method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<ul>
<li>상품명 <input type="text" name="itemName"></li>
<li>파일<input type="file" name="file" ></li>
</ul>
<input type="submit"/>
</form>
</div> <!-- /container -->
</body>
</html>
여기서 상품명은 itemName이라는 이름으로 올라가고 파일은 file이라는 이름으로 올라간다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
public class ServletUploadcontrollerV1 {
@GetMapping("/upload")
public String newFile(){
return "upload-form";
}
@PostMapping("/upload")
public String saveFileV1(MultipartHttpServletRequest request) throws ServletException, IOException {
log.info("request={}",request);
String itemName= request.getParameter("itemName");
log.info("itemName={}",itemName);
Collection<Part> parts = request.getParts();
log.info("parts= {}",parts);
return "upload-form";
}
}
itemName은 알다시피 request.getParameter()로 받을 수 있고 파일은 다르게 받는다.
Part타입으로 받는 것을 알 수 있고 로그로 어떻게 넘어오는지 확인해보자.
request부터 보면 원래는 HttpServletRequest를 사용하는데 multipart의 전송방식으로 보내면 HttpServletRequest를 상속받은 StandardMultipartHtppServletRequest를 사용한다. 이것으로 바이너리 파일 등을 전송할 수 있다. 이 과정에서 멀티파트 리졸버가 멀티파트 요청일 때 서블릿 컨테이너가 전달하는 일반적인 servletrequest를 multipartservletrequest로 바꿔준다.
이후엔 그냥 MultipartFile이라는 것을 사용하는 것이 더 편하기 때문에 MultipartHttpServletRequest는 잘 사용하지 않는다.
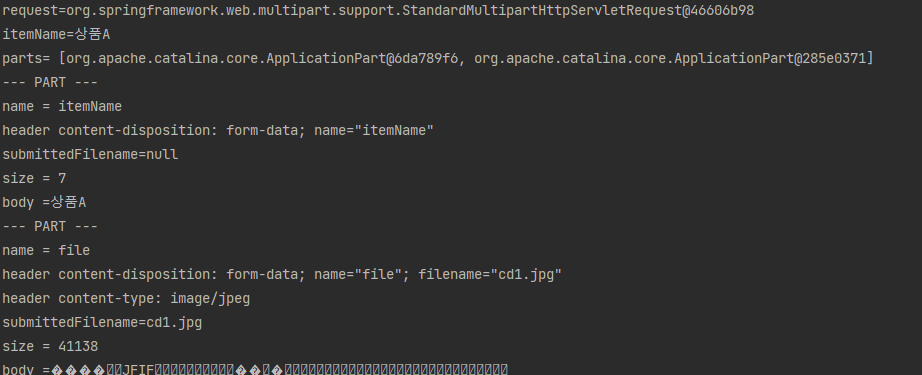
그리고 itemName으로는 우리가 쓴 이름이 나오고 parts 부분에 전송한 파일들이 있다.
그리고 또다른 로그를 보면 Content-Disposition이라는 항목별 헤더가 보이고 문자는 그냥 문자를 출력해주고 파일은 그 파일의 확장자까지 알려준다.
저장
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
@Slf4j
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/servlet/v2")
public class ServletUploadcontrollerV2 {
@Value("${file.dir}")
private String fileDir;
@GetMapping("/upload")
public String newFile(){
return "upload-form";
}
@PostMapping("/upload")
public String saveFileV1(MultipartHttpServletRequest request) throws ServletException, IOException {
log.info("request={}",request);
String itemName= request.getParameter("itemName");
log.info("itemName={}",itemName);
Collection<Part> parts = request.getParts();
log.info("parts= {}",parts);
for (Part part : parts) {
log.info("--- PART ---");
log.info("name = {} ", part.getName());
Collection<String> headerNames = part.getHeaderNames();
for (String headerName : headerNames) {
log.info("header {}: {}", headerName, part.getHeader(headerName));
}
//편의 메서드
// content-idsposition; filename
log.info("submittedFilename={}", part.getSubmittedFileName());
log.info("size = {} ",part.getSize()); //part body size
//데이터 읽기
InputStream inputStream = part.getInputStream();
String body = StreamUtils.copyToString(inputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
log.info("body ={}",body);
//파일에 저장하기
if(StringUtils.hasText(part.getSubmittedFileName())){
String fullPath = fileDir + part.getSubmittedFileName();
log.info("파일 저장 fullPath = {}", fullPath);
part.write(fullPath);
}
}
return "upload-form";
}
}
part 주요 메서드
- part.getSubmittedFileName(): 클라이언트가 전달한 파일명
- part.getInpuStream(): Part의 전송 데이터를 읽을 수 있다.
- part.write(…): Part를 통해 전송된 데이터를 저장할 수 있다.
각각 part를 보면 문자는 submittedFilename은 없다. 파일이 없으니 당연하다. 파일부분에서는 헤더가 2개가 있다. 기본 헤더인 content-disposition과 content-type이 그것이다 2번째 헤더는 확장자를 나타낸다.
스프링 파일 업로드/저장
스프링 부터는 MultipartFile이라는 인터페이스로 간단하게 멀티파트 파일을 지원한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
@Slf4j
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/spring")
public class SpringUploadController {
@Value("${file.dir}")
private String fileDir;
@GetMapping("/upload")
public String newFile(){
return "upload-form";
}
@PostMapping("/upload")
public String saveFile(@RequestParam String itemName,
@RequestParam MultipartFile file, HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {
log.info("request = {}", request);
log.info("itemName = {}", itemName);
log.info("multipartFile = {}", file);
if(!file.isEmpty()){
String fullPath = fileDir + file.getOriginalFilename();
log.info("파일 저장 fullPath = {} ", fullPath);
file.transferTo(new File(fullPath));
}
return "upload-form";
}
}
Multipartfile 주요 메서드
file.getOriginalFilename(): 업로드 파일 명
file.transferTo(…): 파일저장
미리 지정해둔 path와 multipartfile의 객체에 대한 정보 로그도 잘 나온다.
파일 다운로드
jsp(view)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
<c:forEach var="file" items="${article.fileInfos}">
<li>${file.originalFile}
<a href="#" class="filedown"
sfolder="${file.saveFolder}"
sfile="${file.saveFile}"
ofile="${file.originalFile}">[다운로드]
</a>
</c:forEach>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
<form id="downform" action="${root}/board/download">
<input type="hidden" name="sfolder">
<input type="hidden" name="ofile">
<input type="hidden" name="sfile">
</form>
let files = document.querySelectorAll(".filedown");
files.forEach(function(file) {
file.addEventListener("click", function() {
document.querySelector("[name='sfolder']").value = file.getAttribute("sfolder");
document.querySelector("[name='ofile']").value = file.getAttribute("ofile");
document.querySelector("[name='sfile']").value = file.getAttribute("sfile");
document.querySelector("#downform").submit();
});
});
다운로드 버튼을 누르면 각 파일의 정보가 hidden form으로 들어가고 전송된다.
sfolder는 저장된 경로를 뜻하고 ofile은 원래 파일이름 sfile은 고유화로 저장될 파일의 이름이다.
자바(controller)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
@GetMapping(value = "/download")
public ModelAndView downloadFile(@RequestParam("sfolder") String sfolder,
@RequestParam("ofile") String ofile,
@RequestParam("sfile") String sfile,
HttpSession session) {
MemberDto memberDto = (MemberDto) session.getAttribute("userinfo");
if (memberDto != null) {
Map<String, Object> fileInfo = new HashMap<String, Object>();
fileInfo.put("sfolder", sfolder);
fileInfo.put("ofile", ofile);
fileInfo.put("sfile", sfile);
return new ModelAndView("fileDownLoadView", "downloadFile", fileInfo);
} else {
return new ModelAndView("redirect:/");
}
}
여기에선 들어온 정보를 하나의 Map객체로 다 받는다. 그리고 그 객체를 downloadFile이라는 이름으로 fileDownLoadView.java로 향한다.
자바(model)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
public class FileDownLoadView extends AbstractView {
public FileDownLoadView() {
setContentType("apllication/download; charset=UTF-8");
}
@Override
protected void renderMergedOutputModel(Map<String, Object> model,
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
ServletContext ctx = getServletContext();
String realPath = ctx.getRealPath("/upload");
// 전송받은 모델(파일 정보)
Map<String, Object> fileInfo = (Map<String, Object>) model.get("downloadFile");
String saveFolder = (String) fileInfo.get("sfolder"); // 파일 경로
String originalFile = (String) fileInfo.get("ofile"); // 원본 파일명(화면에 표시될 파일 이름)
String saveFile = (String) fileInfo.get("sfile"); // 암호화된 파일명(실제 저장된 파일 이름)
File file = new File(realPath + File.separator + saveFolder, saveFile);
response.setContentType(getContentType());
response.setContentLength((int) file.length());
String header = request.getHeader("User-Agent");
boolean isIE = header.indexOf("MSIE") > -1 || header.indexOf("Trident") > -1;
String fileName = null;
// IE는 다르게 처리
if (isIE) {
fileName = URLEncoder.encode(originalFile, "UTF-8").replaceAll("\\+", "%20");
} else {
fileName = new String(originalFile.getBytes("UTF-8"), "ISO-8859-1");
}
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment; filename=\"" + fileName + "\";");
response.setHeader("Content-Transfer-Encoding", "binary");
OutputStream out = response.getOutputStream();
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
FileCopyUtils.copy(fis, out);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(fis != null) {
try {
fis.close();
}catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
out.flush();
}
}
- 먼저 realPath를 얻기 위해 ServeltContext객체를 가져온다.
- downloadFile의 이름으로 보내온 Map객체를 받는다.
- sfolder, ofile, sfile을 문자열로 받아 놓는다.
- 그리고 File객체를 만든다( 여기서 File.separator는 운영체제에 맞는 구분자를 맞춰주기 위함)
- response.setContentType()은 파일의 확장자별로 다른데 getContentType()으로 각각의 파일 확장자에 맞는 contentType으로 설정
- setContentLength는 파일의 용량을 설정하는데 우리가 갖고 있는 file의 길이를 알려주면 된다.
- request.getHeader(”User-Agent”)는 요청을 보낸 사용자에 기반한 브라우저와 운영체제 정보가 들어있다.
- isIE라는 boolean 변수를 만든다. 이것은 인터넷익스플로러는 따로 처리해야하기 때문에 위에서 가져온 header에서 IE를 분리 해낸다.
- 인코딩을 해야하는데 IE는 URLEncoder.encode()로 utf-8로 인코딩을 한다.
- 나머지 브라우저는 new String의 생성자 선에서 처리가 가능하다.
- response.setHeader에서 Content-Disposition헤더에 attachment를 주면 다운로드를 받을 때 다운로드 박스가 뜬다. inline옵션을 주면 웹에서 바로 파일을 열어버린다.
- 또다른 header인 Content-Transfer-encoding은 전송 인코딩 설정이다. 파일이므로 binary를 해준다.
- FileCopyUtils.copy()에선 인자를 2개 받는데 순서대로 from, to의 개념이라고 보면 된다.
- from에는 다운로드 받을 파일을 stream으로 감싼다.
- to에는 response에 있는 OutputStream을 가져온다.



Comments powered by Disqus.